This blog dwhdatawarehousing.blogspot.com briefly describes the Data Warehousing components and its related contents. This is helpfull for people who's preparing for ETL interviews.
Thursday, November 9, 2017
Star Schema & Snowflakes Schema
qStar
Schema
vThere will be a
centrally located fact table which is surrounded by one or many dimension
table. This design looks like a star so
its called as Star Schema
vDimensions in Star
Schema are De-normalized
vBenefit of star
schema is Query performance will be very high as there will not be joins and
only disadvantage is it requires more disk space
qSnowflakes
Schema
Types of Facts
qTypes
of Facts
vAdditive: All the
KPIs are group by
Eg: Sales Fact
Quantity like sum(),avg() etc
vSemi Additive: Some
KPIs are group by
Eg: Account balance. A sum()
function on balance does not give a useful result but max() or min() balance
might be useful. Consider price rate or currency rate. Sum is meaningless on
rate; however, average function might be useful.
vNon_Additive: Non-additive
measures are those which can not be used inside any numeric aggregation function like sum(),
Avg()
Eg: Ratio ,
percentage
vFact_less_fact: Does
not contains any measures only KPIs
KPI: Key performance Indicator
Types of Dimensions
qTypes of Dimensions-I
vConfirmed: Shared by two or
more fact tables
Eg: The date dimension
table connected to the sales facts is identical to the date dimension connected
to the inventory facts.
vJunk: A junk dimension is a
collection of random transactional codes it gives convenient place to store Junk Attributes
Eg: instead of
using two different key Combine gender and marital dimension and create one
junk dimension and use that key in the fact table .
vDe-generated
: Derived from Fact
table. Does not have it own dimension
Eg: Transational
Code in a fact table(Invoice)
vRole_playing:
Dimension often used
for multiple purpose and can be joined to more than one foreign key in the fact
table.
Eg: fact table may include
foreign keys for both ship date and delivery date
vInferred: Solution to not yet
ready dimension.
Eg: Generate a
surrogate Key as null for other attributes
vStatic : Not extracted from the
original data source, but are created within the context of the data warehouse.
A static dimension can be loaded manually
Eg: status codes or it can be
generated by a procedure, such as a date or time dimension.
vRapidly Changing Dimension(RCD):Changes frequently. lot of changes happens in a
attributes of a dimension table
vSlowly Changing Dimension(SCD):Changes slowly over a period of time
Types:
• SCD1: To every insert
in source it will insert into target and to every update in the source it will
update in the target. Contains only current records. override old value
•SCD2: To
every insert in source it will insert into target and to every update in the
source it will insert in the target with different Surrogate key. It contains
historical record.(It can be implemented using flagging ,versioning or date
range methods).it add a new row.
•SCD3: It
contains partially historical records(like last 2 or 3 history).it adds a new
row
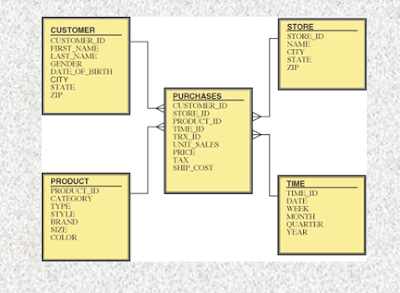
What's Fact & Dimension tables?
qWhat is Dimension
Table?
vDimension
contains descriptive
attributes(data) about a subject.
vThe
table which describe the dimension called Dimension table.
vA
dimension table has a primary key column that uniquely identifies each
dimension record (row).
vE,g:
‘Company’ is a subject Employee, Department and date is Object(dimension
tables) .ID,Name,Dept Nm, joining Dt , Release Dt are attributes(columns).
qWhat is Fact Table?
vFact
is something that is measurable. It
contains only numeric value which can be aggregated.
vA
fact table contains information about KPIs and measure.
vKPI
stands for Key
Performance Indicator which is nothing but Dimension tables Primary Key
vMeasures
are data elements
that can be summed, averaged, or mathematically manipulated
Example:
•Above
customer ,store ,product and time tables are dimension tables which contain
attributes
•Purchase
is the fact table which contains all PKs of dimension tables and price and tax
column which are measures.
What is ETL?
qWhat
is ETL?
vStands for Extract Transform Load. It Extracts data
from multiple data sources ,transform( filter, aggregate, etc) according to the
business rules and then load it into target(ODS/DWH).
vETL Tools:
Informatica Power Center ,Data stage, Oracle Warehouse Builder, SQL Server Integration Services, Data Migrator(IBI)
What is ODS(Operational Data Store) & Staging area ?
q What is ODS?
vStands
for Operational data store
vContains
current data for a limited period of time.(DWH stores periodic data).
vShould
be refreshed daily to get current data(daily or hourly)
vUse
to monitor the business.
vSits
between Staging and DWH
q What is Staging Area?
vParking
area used to dump and integrate data
from heterogeneous source systems
vUse to cleanse data,
apply multiple business rules, filter it and then push it to your Data
Warehouse /ODS
What is Data Mart in Data Warehousing?
vData mart is the
Subset of a data warehouse.
vIt’s a smaller form
of DWH which contain only one subject area.
vTime taken to create
Data Mart in very less
compare to DWH
vTypes of Data Mart
1.Dependant : Dependant on DWH which
draw data from DWH(Draw data from Central DWH which is already created)
E,g:Retails
2. Independent: Independent on DWH or
stand alone DM which draws data directly from Operational or external sources. E,g: Banking
projects,start ups
3.Hybrid: Draw data both from External sources and DWH
q Approaches to create
data Mart
vTwo types of approaches.
Top Down and bottom up
Top Down:
1.First Data warehouse will be created then
data mart.(dependant DM)
2.It directly
built from OLTB
3.Advantage
is all the information is located in one centrally location.
4.Disadvantage is it becomes very big projects and should be handled
by experts .Expensive
Bottom up:
1. First Data
Marts will be created then DWH(Independent DM)
2.Quick approach
3.Easier to manage
4. less expensive
What is Data Warehousing & why ?
qWhat
is Data Warehouse?
vA centrally located
database which is used to store consolidate data from different databases from
different location.
vStores historical
data (not transactional data) to analyze the business and helps in creating Reports.
v As said by Bill
Inmon DWH is a Subject
oriented , Integrated, Non-Volatile and
Time variant Database
vData in DWH is not
Normalized
vDWH is separated from
Organizations operational DBs
vData in DWH would not
be refreshed Daily(should be a specific interval)
qWhy
Data Warehousing is ?
vThe
main purpose of a DW
is to speed-up (simplify) reporting and analytic. It enables slicing and dicing
of data in any way a business user can think of.
vMany
big complex selects
(possibly compared to few inserts, updates and deletes) that just take to long
to execute (and are complicated
to write)
vIf
data from different
systems needs to get combined
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
-
q What is Dimension Table? v Dimension contains descriptive attributes(data) about a subject. v The table which describe the dimensio...